Abstract
Aims: Although ambient assisted living (AAL) environments and serious games for healthcare have been proposed as solutions to meet the changing demographics, the two approaches are rarely combined. We present the development and empirical evaluation of two serious games for healthcare in AAL. The first uses a cooking scenario for training of cognitive functioning. The latter uses a gardening scenario and motion capture for training agility and endurance. As the frequent lack of social acceptance is a major challenge in consumer health technology, we integrated methods of technology acceptance research by means of the UTAUT2-model and intention to use into the evaluation.
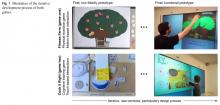
Subject and methods: We developed both games utilizing user-centered and participatory design methods ranging from low-fidelity paper prototypes to usability and acceptance evaluations of functional prototypes. In the final evaluation, each game prototype was evaluated by 64 participants form different age groups.
Results: The results show that although performance decreases with age, the performance attained in the games is not decisive for social acceptance measured as intention to use. However, user diversity factors shape the evaluation of the games, and older people and people with low technical competence are in danger of being excluded from using serious games for healthcare.
Conclusion: Exercise games, if designed right, can mitigate the negative effects of demographic change. Nevertheless, user diversity needs must be considered to ensure that the games are usable and used by a broad audience. The article concludes with guidelines and open research questions for the design of serious games in AAL environments.
Subject and methods: We developed both games utilizing user-centered and participatory design methods ranging from low-fidelity paper prototypes to usability and acceptance evaluations of functional prototypes. In the final evaluation, each game prototype was evaluated by 64 participants form different age groups.
Results: The results show that although performance decreases with age, the performance attained in the games is not decisive for social acceptance measured as intention to use. However, user diversity factors shape the evaluation of the games, and older people and people with low technical competence are in danger of being excluded from using serious games for healthcare.
Conclusion: Exercise games, if designed right, can mitigate the negative effects of demographic change. Nevertheless, user diversity needs must be considered to ensure that the games are usable and used by a broad audience. The article concludes with guidelines and open research questions for the design of serious games in AAL environments.
Brauner P, Ziefle M (2021) Social acceptance of serious games for physical and cognitive training in older adults residing in ambient assisted living environments. Journal of Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-021-01524-y
Related Project(s):